SpringBoot高级篇JdbcTemplate之数据查询上篇 讲了如何使用JdbcTemplate进行简单的查询操作,主要介绍了三种方法的调用姿势 queryForMap, queryForList, queryForObject 本篇则继续介绍剩下的两种方法使用说明
I. 环境准备
环境依然借助前面一篇的配置,链接如: 190407-SpringBoot高级篇JdbcTemplate之数据插入使用姿势详解
或者直接查看项目源码: https://github.com/liuyueyi/spring-boot-demo/blob/master/spring-boot/101-jdbctemplate
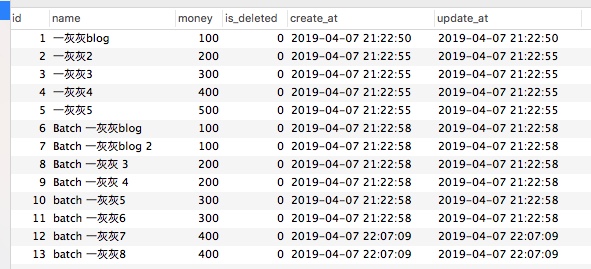
我们查询所用数据,正是前面一篇插入的结果,如下图
II. 查询使用说明
1. queryForRowSet
查询上篇中介绍的三种方法,返回的记录对应的结构要么是map,要么是通过RowMapper进行结果封装;而queryForRowSet方法的调用,返回的则是SqlRowSet对象,这是一个集合,也就是说,可以查询多条记录
使用姿势也比较简单,如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public void queryForRowSet() {
String sql = "select * from money where id > 1 limit 2";
SqlRowSet result = jdbcTemplate.queryForRowSet(sql);
while (result.next()) {
MoneyPO moneyPO = new MoneyPO();
moneyPO.setId(result.getInt("id"));
moneyPO.setName(result.getString("name"));
moneyPO.setMoney(result.getInt("money"));
moneyPO.setDeleted(result.getBoolean("is_deleted"));
moneyPO.setCreated(result.getDate("create_at").getTime());
moneyPO.setUpdated(result.getDate("update_at").getTime());
System.out.println("QueryForRowSet by DirectSql: " + moneyPO);
}
}
|
对于使用姿势而言与之前的区别不大,还有一种就是sql也支持使用占位方式,如
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
sql = "select * from money where id > ? limit ?";
result = jdbcTemplate.queryForRowSet(sql, 1, 2);
while (result.next()) {
MoneyPO moneyPO = new MoneyPO();
moneyPO.setId(result.getInt("id"));
moneyPO.setName(result.getString("name"));
moneyPO.setMoney(result.getInt("money"));
moneyPO.setDeleted(result.getBoolean("is_deleted"));
moneyPO.setCreated(result.getDate("create_at").getTime());
moneyPO.setUpdated(result.getDate("update_at").getTime());
System.out.println("QueryForRowSet by ? sql: " + moneyPO);
}
|
重点关注下结果的处理,需要通过迭代器的方式进行数据遍历,获取每一列记录的值的方式和前面一样,可以通过序号的方式获取(序号从1开始),也可以通过制定列名方式(db列名)
2. query
对于query方法的使用,从不同的结果处理方式来看,划分了四种,下面逐一说明
a. 回调方式 queryByCallBack
这种回调方式,query方法不返回结果,但是需要传入一个回调对象,查询到结果之后,会自动调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| private void queryByCallBack() {
String sql = "select * from money where id > 1 limit 2";
jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new RowCallbackHandler() {
@Override
public void processRow(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException {
MoneyPO moneyPO = result2po(rs);
System.out.println("queryByCallBack: " + moneyPO);
}
});
}
|
上面的实例代码中,可以看到回调方法中传入一个ResultSet对象,简单封装一个转换为PO的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| private MoneyPO result2po(ResultSet result) throws SQLException {
MoneyPO moneyPO = new MoneyPO();
moneyPO.setId(result.getInt("id"));
moneyPO.setName(result.getString("name"));
moneyPO.setMoney(result.getInt("money"));
moneyPO.setDeleted(result.getBoolean("is_deleted"));
moneyPO.setCreated(result.getDate("create_at").getTime());
moneyPO.setUpdated(result.getDate("update_at").getTime());
return moneyPO;
}
|
在后面的测试中,会看到上面会输出两行数据,也就是说
返回结果中每一条记录都执行一次上面的回调方法,即返回n条数据,上面回调执行n次
前面回调方式主要针对的是不关系返回结果,这里的则是将返回的结果,封装成我们预期的对象,然后返回
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| private void queryByResultSet() {
String sql = "select * from money where id > 1 limit 2";
List<MoneyPO> result = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new ResultSetExtractor<List<MoneyPO>>() {
@Override
public List<MoneyPO> extractData(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException, DataAccessException {
List<MoneyPO> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (rs.next()) {
list.add(result2po(rs));
}
return list;
}
});
System.out.println("queryByResultSet: " + result);
}
|
额外注意下上面你的使用,如果返回的是多条数据,注意泛型参数类型为List<?>, 简单来说这是一个对结果进行批量转换的使用场景
因此在上面的extractData方法调用时,传入的是多条数据,需要自己进行迭代遍历,而不能像第一种那样使用
c. 结果单行处理 RowMapper
既然前面有批量处理,那当然也就有单行的转换方式了,如下
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| private void queryByRowMapper() {
String sql = "select * from money where id > 1 limit 2";
List<MoneyPO> result = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new RowMapper<MoneyPO>() {
@Override
public MoneyPO mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
return result2po(rs);
}
});
System.out.println("queryByRowMapper: " + result);
}
|
在实际使用中,只需要记住RowMapper方式传入的是单条记录,n次调用;而ResultSetExtractor方式传入的全部的记录,1次调用
d. 占位sql
前面介绍的几种都是直接写sql,这当然不是推荐的写法,更常见的是占位sql,通过传参替换,这类的使用前一篇博文介绍得比较多了,这里给出一个简单的演示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| private void queryByPlaceHolder() {
String sql = "select * from money where id > ? limit ?";
List<MoneyPO> result = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new RowMapper<MoneyPO>() {
@Override
public MoneyPO mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
return result2po(rs);
}
}, 1, 2);
System.out.println("queryByPlaceHolder: " + result);
}
|
e. PreparedStatement 方式
在插入记录的时候,PreparedStatement这个我们用得很多,特别是在要求返回主键id时,离不开它了, 在实际的查询中,也是可以这么用的,特别是在使用PreparedStatementCreator,我们可以设置查询的db连接参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| private void queryByPreparedStatement() {
List<MoneyPO> result = jdbcTemplate.query(new PreparedStatementCreator() {
@Override
public PreparedStatement createPreparedStatement(Connection con) throws SQLException {
con.setReadOnly(true);
PreparedStatement statement = con.prepareStatement("select * from money where id > ? limit ?");
statement.setInt(1, 1);
statement.setInt(2, 2);
return statement;
}
}, new RowMapper<MoneyPO>() {
@Override
public MoneyPO mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
return result2po(rs);
}
});
System.out.println("queryByPreparedStatement: " + result);
}
|
上面是一个典型的使用case,当然在实际使用JdbcTemplate时,基本不这么玩
f. 查不到数据场景
前面一篇查询中,在单个查询中如果没有结果命中sql,会抛出异常,那么这里呢?
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| private void queryNoRecord() {
List<MoneyPO> result = jdbcTemplate
.query("select * from money where id > ? limit ?", new Object[]{100, 2}, new RowMapper<MoneyPO>() {
@Override
public MoneyPO mapRow(ResultSet rs, int rowNum) throws SQLException {
return result2po(rs);
}
});
System.out.println("queryNoRecord: " + result);
}
|
从后面的输出结果会看出,没有记录命中时,并没有什么关系,上面会返回一个空集合
III. 测试&小结
1. 测试
接下来测试下上面的输出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| package com.git.hui.boot.jdbc;
import com.git.hui.boot.jdbc.insert.InsertService;
import com.git.hui.boot.jdbc.query.QueryService;
import com.git.hui.boot.jdbc.query.QueryServiceV2;
import com.git.hui.boot.jdbc.update.UpdateService;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
private QueryServiceV2 queryServiceV2;
public Application(QueryServiceV2 queryServiceV2) {
this.queryServiceV2 = queryServiceV2;
queryTest2();
}
public void queryTest2() {
queryServiceV2.queryForRowSet();
queryServiceV2.query();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class);
}
}
|
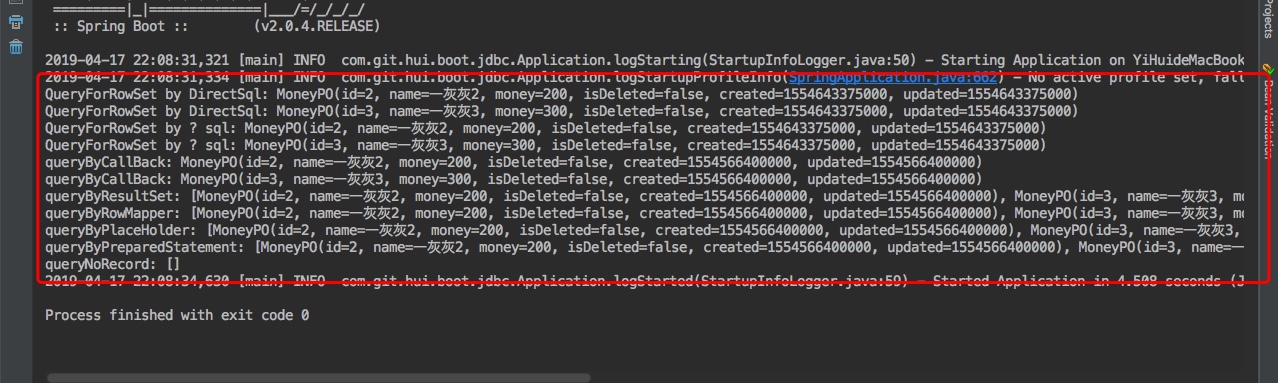
上面执行输出结果如下
2. 小结
本文主要介绍了另外两种查询姿势, queryForRowSet 与 query
queryForRowSet
- 返回
SqlRowSet对象,需要遍历获取所有的结果
query
- 提供三种结果处理方式
- 不返回结果的回调姿势
- 对结果批量处理的方式
ResultSetExtractor
- 对结果单个迭代处理方式
RowMapper
- 可以返回>=0条数据
- 如果需要对查询的连接参数进行设置,使用
PreparedStatementCreator来创建PreparedStatement方式处理
IV. 其他
相关博文
0. 项目
1. 一灰灰Blog
一灰灰的个人博客,记录所有学习和工作中的博文,欢迎大家前去逛逛
2. 声明
尽信书则不如,以上内容,纯属一家之言,因个人能力有限,难免有疏漏和错误之处,如发现bug或者有更好的建议,欢迎批评指正,不吝感激
3. 扫描关注
一灰灰blog

知识星球
打赏
如果觉得我的文章对您有帮助,请随意打赏。

微信打赏

支付宝打赏






