06.工具调用 FunctionCalling
06.工具调用 FunctionCalling
我们知道大模型是基于一系列数据进行训练的,且每次训练的成本很高;那么大模型是怎么样表现得十八般武艺样样精通的呢?
function calling就是设计出来给大模型当外挂的瑞士工具包,通过给大模型设计一个与外部工具进行交互的方式,来扩展大模型在训练时缺失或者不够与时俱进的能力
一、工作原理
SpringAi 提供了完备工具调用封装,可以非常方便的将本地方法封装成工具,供大模型调用
1. 工具调用流程
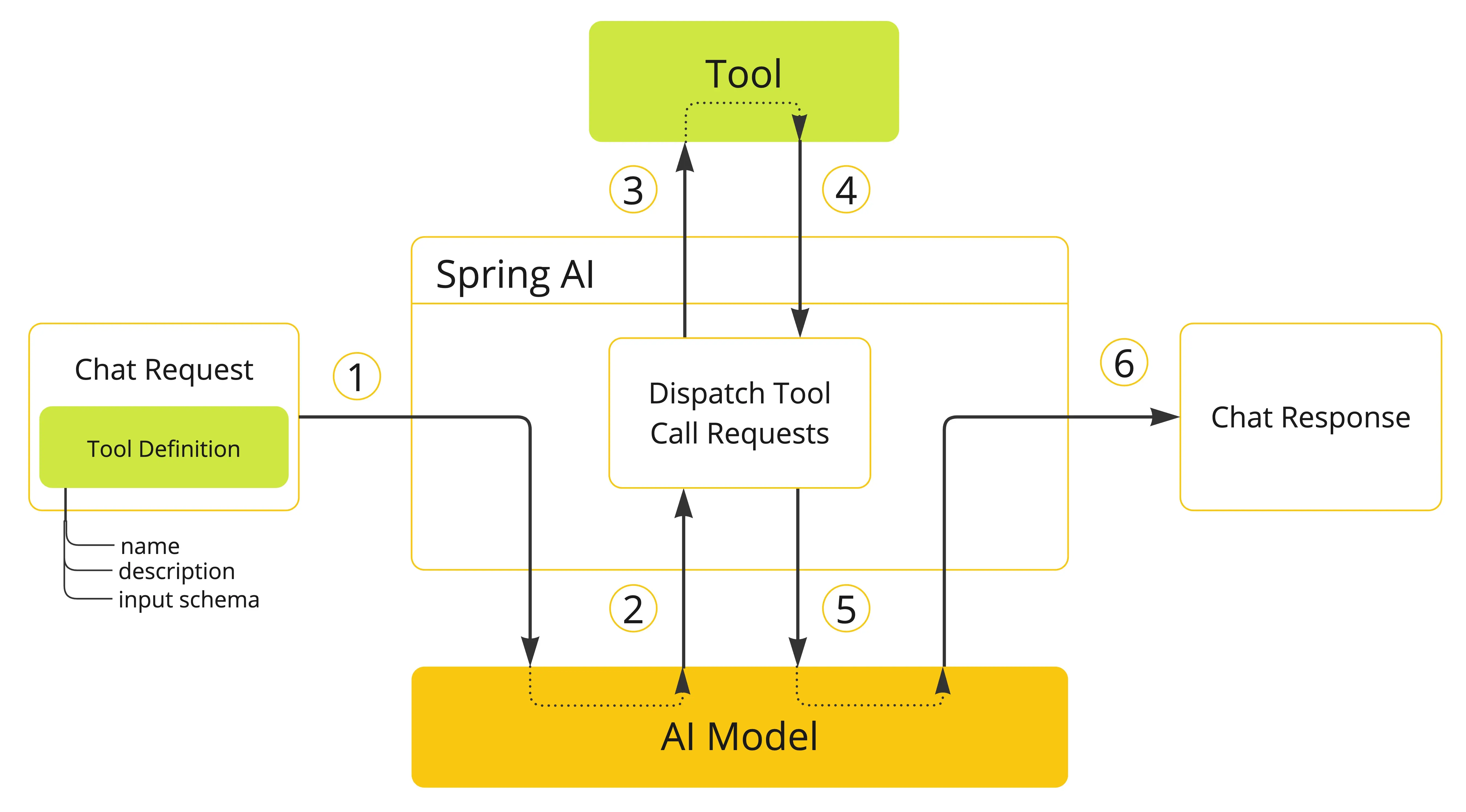
工具调用流程如下:
- 在向大模型发起请求时,将工具信息传递给大模型
- 每个工具的定义都包含名称、描述、输入参数
- 大模型根据工具信息,会发送包含工具名称、亲求参数的请求给工具服务
- 应用程序根据工具名称,识别到对应的工具,调用工具方法
- 工具执行结果返回给应用程序进行处理(可能是直接返回给用户,也可能是返回给大模型)
- 应用程序将工具执行结果返回给大模型
- 大模型利用工具返回的结果,构建返回结果给用户
2. SpringAI关键实现
SpringAI主要提供了两种内置方式将本地方法封装成工具
- 声明式:通过注解
@Tool - 编程式:通过底层的
MethodToolCallbackFunctionToolCallback
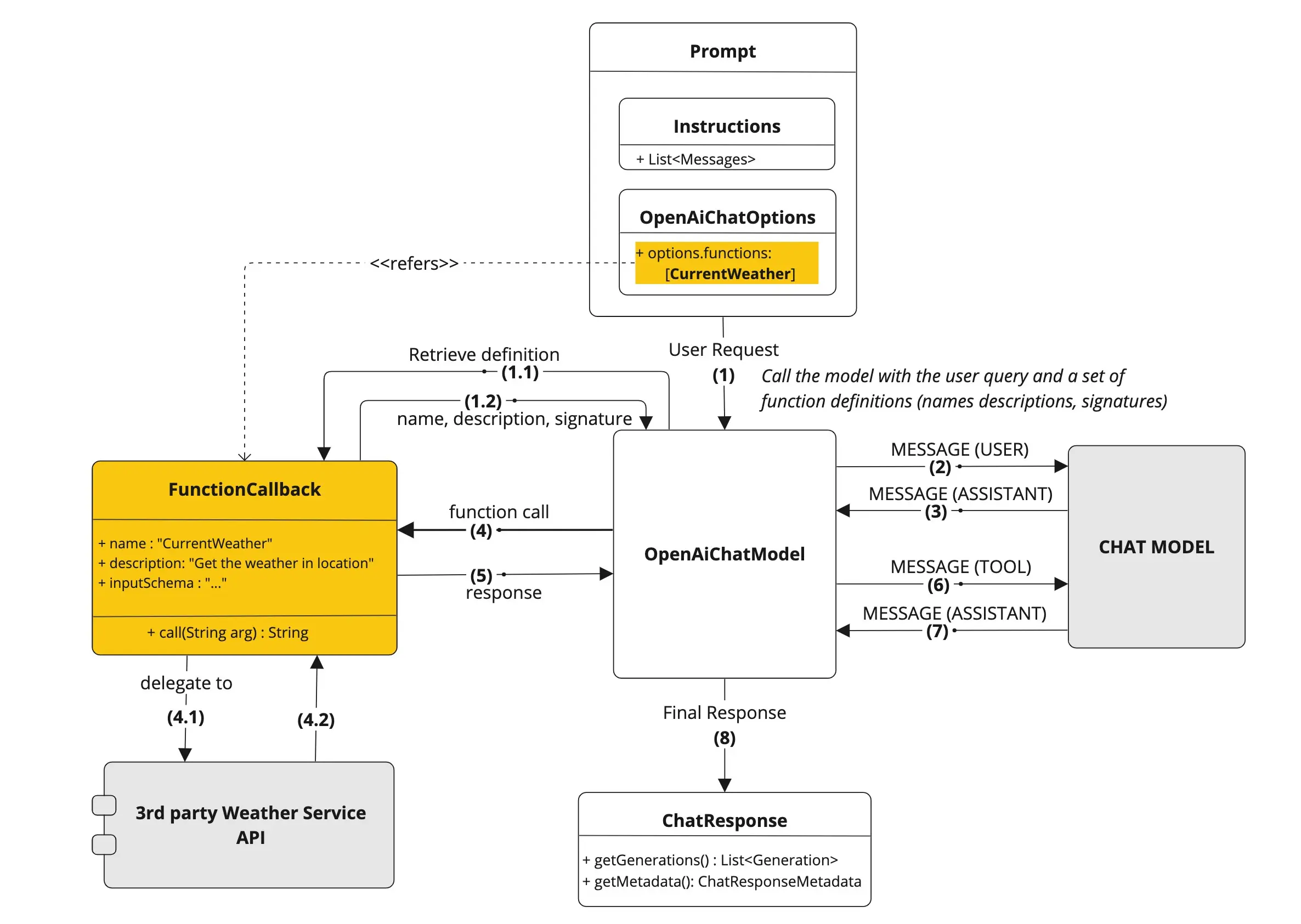
上图中橙色的部分,就是SpringAI将我们本地方法封装成工具,供大模型进行交互;接下来我们看一下SpringAI的关键类
a. ToolCallback
ToolCallback 接口提供了定义 AI 模型可调用工具的方式,包含工具定义和执行逻辑。
public interface ToolCallback {
ToolDefinition getToolDefinition();
default ToolMetadata getToolMetadata() {
return ToolMetadata.builder().build();
}
String call(String toolInput);
default String call(String toolInput, @Nullable ToolContext tooContext) {
if (tooContext != null && !tooContext.getContext().isEmpty()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Tool context is not supported!");
} else {
return this.call(toolInput);
}
}
}
SpringAI提供了两种内置实现
- MethodToolCallback: 将本地方法定义为AI模型可调用的工具
- FunctionToolCallback: 将函数定义为AI模型可调用的工具
b. ToolDefinition
ToolDefinition 接口提供 AI 模型识别工具可用性所需的信息,包括工具名称、描述及输入模式。每个 ToolCallback 实现必须提供 ToolDefinition 实例来定义工具。
public interface ToolDefinition {
/**
* 工具名
*/
String name();
/**
* 工具说明,告诉AI这个工具可以干嘛
*/
String description();
/**
* 传参方式,通常是 json schema格式
*/
String inputSchema();
}
若需要手动创建的工具定义,可以使用ToolDefinition.Builder
ToolDefinition toolDefinition = ToolDefinition.builder()
.name("currentWeather")
.description("Get the weather in location")
.inputSchema("""
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["C", "F"]
}
},
"required": ["location", "unit"]
}
""")
.build();
除了上面的方式,对于本地java方法,可以直接通过反射的方式来生成基于方法的工具定义
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getCurrentDateTime");
ToolDefinition toolDefinition = ToolDefinition.from(method);
// 如果需要显示修改某些属性,可以如下
ToolDefinition toolDefinition = ToolDefinition.builder(method)
.name("currentDateTime")
.description("Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
.inputSchema(JsonSchemaGenerator.generateForMethodInput(method))
.build();
c. JSON Schema
向 AI 模型提供工具时,模型需要知道工具调用输入类型的模式,Spring AI 通过 JsonSchemaGenerator 类内置支持生成工具输入类型的 JSON Schema
下面是一个json schema的示例(在前面结构化返回中,实际上也用到了 JSON Schema,用于告知大模型如何返回我们希望格式的数据)
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"location": {
"type": "string"
},
"unit": {
"type": "string",
"enum": ["C", "F"]
}
},
"required": ["location", "unit"]
}
这里的json schema主要用于方法/函数调用的传参定义,SpringAI内置支持下面四种基于注解升成输入参数描述、是否必传
Spring AI的@ToolParam(description = "…", required=false): 参数描述 + 是否必传Jackson的@JsonClassDescription(description = "…): 参数描述Jackson的@JsonPropertyDescription(description = "…"): 参数描述Jackson的@JsonProperty(required = false): 参数是否必传Swagger的@Schema(description = "…", required = false): 参数描述 + 是否必传Spring的@Nullable: 参数是否必传
示例:
class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "Set a user alarm for the given time")
void setAlarm(@ToolParam(description = "Time in ISO-8601 format", required = true) String time) {
LocalDateTime alarmTime = LocalDateTime.parse(time, DateTimeFormatter.ISO_DATE_TIME);
System.out.println("Alarm set for " + alarmTime);
}
}
d. 结果转换
通常方法/函数返回的是Object对象,需要转换给大模型使用,SpringAI定义ToolCallResultConverter对返回进行序列化,实现将返回结果转换为String对象
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ToolCallResultConverter {
/**
* Given an Object returned by a tool, convert it to a String compatible with the
* given class type.
*/
String convert(@Nullable Object result, @Nullable Type returnType);
}
SpringAI默认的结果转换为基于Jackson的json序列化(DefaultToolCallResultConverter),当然如果你喜欢,也可以换成gson、fastjson或者自定义的转换实现
e. ToolContext
Spring AI 支持通过 ToolContext API向工具传递额外的上下文信息,ToolContext 中的数据由用户调用 ChatClient 时提供。后面的使用示例会进行案例介绍
public final class ToolContext {
public static final String TOOL_CALL_HISTORY = "TOOL_CALL_HISTORY";
private final Map<String, Object> context;
public ToolContext(Map<String, Object> context) {
this.context = Collections.unmodifiableMap(context);
}
public Map<String, Object> getContext() {
return this.context;
}
public List<Message> getToolCallHistory() {
return (List)this.context.get("TOOL_CALL_HISTORY");
}
}
ToolContext的实现也非常简单,一个不可变对象Map来承接工具调用上下文数据
二、使用示例
1. 项目创建
项目创建方式与之前并无差别,创建一个SpringBoot项目,并引入SpringAI的依赖,有需要的小伙伴参考 创建一个SpringAI-Demo工程
在pom中添加相关依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.ai</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-ai-starter-model-zhipuai</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
我们这里使用智谱的免费大模型,虽然免费但它依然支持工具调用(请注意,并不是所有的模型都支持工具调用的,在使用之前到官方的说明确认是否支持)
2. 声明式使用方式
我们定义一个简单、基础可用的工具方法,主要用于获取当前时间,核心点就是在方法上添加注解 @Tool
- 注解的 description 属性非常重要,用于知道模型判断何时调用这个工具;当描述不够清晰时,可能导致模型在该调用工具时没有调用,或者调用错了工具
class DateTimeTools {
// 获取当前时间,工具描述,使用中文也是可以的
@Tool(description = "Get the current date and time in the user's timezone")
String getCurrentDateTime() {
String ans = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
System.out.println("进入获取当前时间了:" + ans);
return ans;
}
}
对于使用 ChatClient 来使用工具调用,就非常简单了,如
@RestController
public class ChatController {
private final ChatClient chatClient;
public ChatController(ZhiPuAiChatModel chatModel) {
this.chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.build();
}
@RequestMapping(path = "time")
public String getTime(String msg) {
return chatClient.prompt(msg).tools(new DateTimeTools()).call().content();
}
@RequestMapping(path = "timeNoTools")
public String getTimeNoTools(String msg) {
return chatClient.prompt(msg).call().content();
}
}
上面有提供了两个接口, getTime 接口使用了工具,getTimeNoTools 接口没有使用工具;使用方式形如
chatClient.prompt().tools(xxx):通过tools方法注入工具
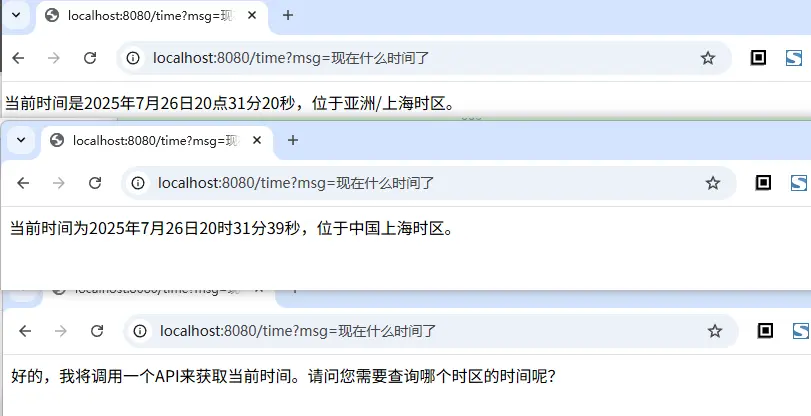
接下来我们看一下表现情况
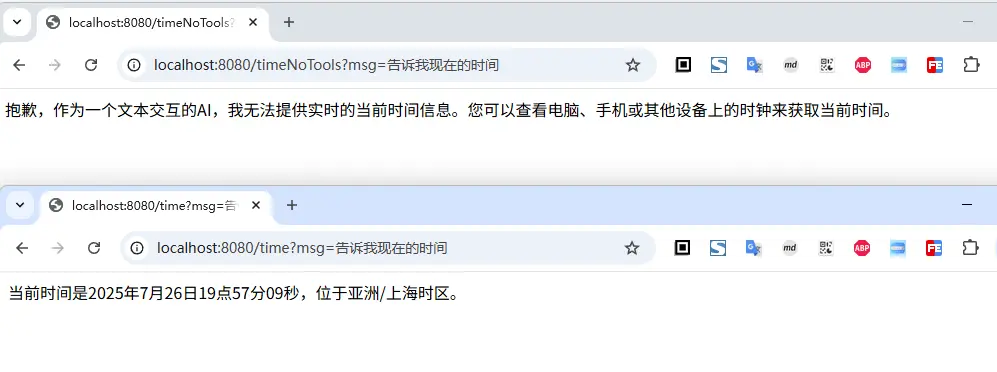
说明:虽然上面的访问对比中,在请求
time接口时,正确的返回了时间,但是大模型并不总是和我们预期的一致,同样的提问,它有时不会主动调用我们注入的工具
3. 带参数的工具方法
前面定义的工具没有参数,接下来我们在看一下带参数的工具方法
在方法参数上,可以通过 @ToolParam 注解对参数进行解释说明(这个注解是非必填的),注解内有两个属性
description:参数描述,用于帮助模型更准确地理解如何使用该参数。例如:参数格式要求、允许取值范围等。required:指定参数是否为必需项(默认值:true,即所有参数默认必需)。
比如我现在定义一个返回不同时区的当前时间的工具,供大模型调用,参数是时区,同样放在 DateTimeTools 类中,这样就可以直接使用上面的api
class DateTimeTools {
@Tool(description = "传入时区,返回对应时区的当前时间给用户")
String getTimeByZoneId(@ToolParam(description = "需要查询时间的时区") ZoneId area) {
// 根据时区,查询对应的时间
ZonedDateTime time = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(area);
// 转换为 2025-07-26 20:00:00 格式的字符串
// 将输入时区的时间转换为本地时区
ZonedDateTime localTime = time.withZoneSameInstant(ZoneId.systemDefault());
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String ans = localTime.format(formatter);
System.out.println("传入的时区是:" + area + "-" + ans);
return ans;
}
}
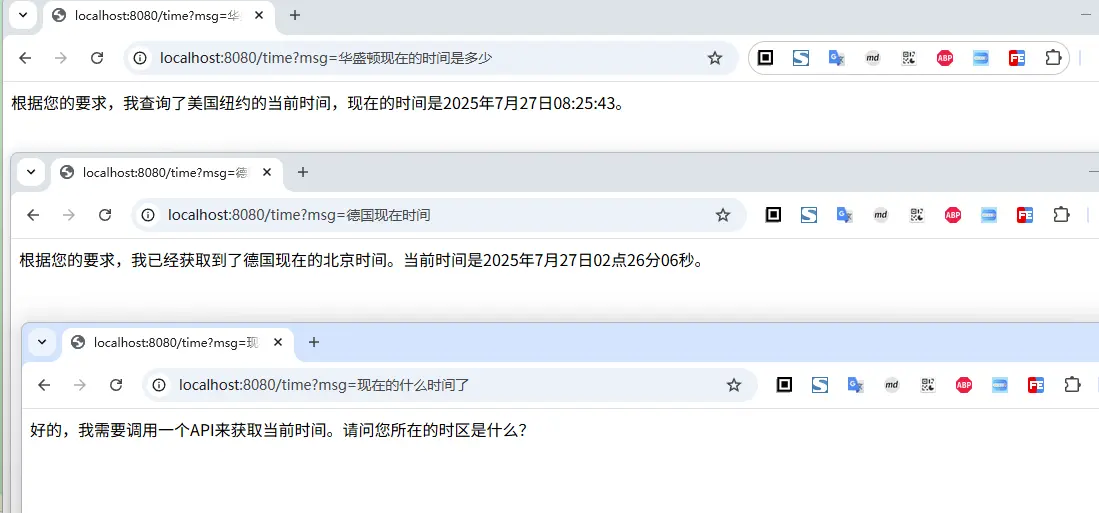
从上面的访问示例也可以看出,我们询问某个地区的时间时,大模型会自动根据地区找到时区,然后调用我们的工具返回结果
但是一个问题来了,直接问时间时,它不会调用我们之前定义的那个方法,返回时间,这是为什么呢?
我们尝试调整一下,之前定义获取当前时间的工具方法说明
@Tool(description = "不需要关注用户时区,直接返回当前的时间给用户")
String getCurrentDateTime() {
String ans = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(LocaleContextHolder.getTimeZone().toZoneId()).toString();
System.out.println("进入获取当前时间了:" + ans);
return ans;
}
然后再多问几次,你就会发现大模型会主动调用我们定义的这个方法,返回时间(但是并不能始终保证它总是表现正确)
- 所以一个何时的、精确的工具描述,对于大模型的决策是否调用,非常重要
4. 添加默认工具
上面介绍的是在用户发起对话时,设置Prompt时指定工具调用,同样的,SpringAI也提供了默认工具的设置方式,在ChatClient创建时,指定默认的工具,这样只要用这个ChatClient进行对话,这些工具都会提供给大模型,而不在需要单独进行设置
使用方式形如
ChatClient chatClient = ChatClient.builder(chatModel)
.defaultTools(new DateTimeTools())
.build();
这个就不做具体的演示了,没有什么特殊的地方
5. ChatModel 添加工具
如果某些场景下,我们不是通过ChatClent而是直接借助ChatModel进行对话,同样也可以添加工具,通过 ChatOptions 来实现
具体的使用姿势如下,借助ToolCallbacks来获取工具集,借助ToolCallingChatOptions来添加工具集
@RequestMapping(path = "showTime")
public String showTime(String msg) {
ToolCallback[] tools = ToolCallbacks.from(new DateTimeTools());
ChatOptions options = ToolCallingChatOptions.builder()
.toolCallbacks(tools)
.build();
return chatModel.call(new Prompt(msg, options)).getResult().getOutput().getText();
}
6. 编程式使用方式
前面介绍的都是基于@Tool注解的声明式定义工具,这种适用于工具实现完全由我们掌控的场景;对于一些非控制的工具实现(如三方sdk),或者需要动态获取工具参数的场景,我们可以使用编程式定义工具
编程式的使用方式,主要是借助MethodToolCallback.Builder来构建我们需要的MethodToolCallback
使用这种方式时,需要重点看一下前面第一节的内容,ToolCallback ToolDefinition的类结构定义,清楚之后,再看下面的参数设置就会更轻轻松(也知道为什么要这么实现)
toolDefinition:定义工具名称、描述及输入模式的ToolDefinition实例(必需项)- 可通过
ToolDefinition.Builder类构建。
- 可通过
toolMetadata: 定义额外设置的ToolMetadata实例,非必需- 可通过
ToolMetadata.Builder类构建 - returnDierect
: 是否直接返回结果(默认为false`),为true时表示直接将结果返回给用户、而不是给大模型进行调用
- 可通过
toolMethod: 工具方法的Method实例 (必需项)toolObject: 包含工具方法的对象实例(若方法为静态方法则可省略此参数)toolCallResultConverter:用于将工具调用结果转换为String对象并返回 AI 模型ToolCallResultConverter实例(未配置时默认使用DefaultToolCallResultConverter)。
@RequestMapping(path = "timeByCodeTool")
public String getTimeByCodeTool(String msg) {
Method method = ReflectionUtils.findMethod(DateTimeTools.class, "getTimeByZoneId", ZoneId.class);
ToolDefinition toolDefinition = ToolDefinition.builder()
.name("getTimeByZoneId")
.description("传入时区,返回对应时区的当前时间给用户")
.inputSchema(JsonSchemaGenerator.generateForMethodInput(method))
.build();
ToolMetadata toolMetadata = ToolMetadata.builder()
.returnDirect(false)
.build();
ToolCallback callBack = MethodToolCallback.builder()
.toolDefinition(toolDefinition)
.toolMetadata(toolMetadata)
.toolMethod(method)
.toolObject(new DateTimeTools())
.build();
return chatClient.prompt(msg).toolCallbacks(callBack).call().content();
}
在使用方法工具时,需要注意一些限制
以下类型目前不支持作为工具方法的参数或返回类型:
- Optional
- 异步类型(如 CompletableFuture、Future)
- 响应式类型 (如 Flow、Mono、Flux)
- 函数式类型(如 Function、Supplier、Consumer)
7. 函数作为工具调用的使用示例
到现在为止,我们都是将方法作为工具给大模型进行调用,在java8+之后,除了方法还有些函数式接口,比如Function、Consumer、Supplier、Predicate等,这些函数式接口也可以作为工具进行调用,使用方式如下:
通过 FunctionToolcallback 来将函数式类型,转换为工具
class NowService implements Function<AreaReq, AreaResp> {
@Override
public AreaResp apply(AreaReq req) {
ZoneId area = req.zoneId();
// 根据时区,查询对应的时间
ZonedDateTime time = LocalDateTime.now().atZone(area);
// 转换为 2025-07-26 20:00:00 格式的字符串
// 将输入时区的时间转换为本地时区
ZonedDateTime localTime = time.withZoneSameInstant(ZoneId.systemDefault());
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String ans = localTime.format(formatter);
System.out.println("传入的时区是:" + area + "-" + ans);
return new AreaResp(ans);
}
}
record AreaReq(@ToolParam(description = "需要查询时间的时区") ZoneId zoneId) {
}
record AreaResp(String time) {
}
@RequestMapping(path = "timeByCodeFunc")
public String getTimeByCodeFunc(String msg) {
// 使用函数式工具需要注意的是,传参和返回结果,要么是void,要么是POJO
ToolCallback callBack = FunctionToolCallback.builder("nowDateByArea", new NowService())
.description("传入时区,返回对应时区的当前时间给用户")
.inputType(AreaReq.class)
// 下面这一行实际是可以省略的,默认就是根据 inputType 进行生成jsonSchema
.inputSchema(JsonSchemaGenerator.generateForType(AreaReq.class))
.toolMetadata(ToolMetadata.builder().returnDirect(false).build())
.build();
return chatClient.prompt(msg).toolCallbacks(callBack).call().content();
}
具体的使用方式,和上面介绍的方法的编程式相差不大,但是有一个需要格外注意的事项
- 函数输入和输出可以是 Void 或 POJO。输入和输出的 POJO 必须是可序列化的,因为结果将被序列化并发送回模型。
- 函数及输入输出类型必须是 public 的。
以下类型目前不支持作为工具函数的输入或输出类型:
- 基本类型
- Optional
- 集合类型 (如 List、Map、Array、Set)
- 异步类型(如 CompletableFuture、Future)
- 响应式类型(如 Flow、Mono、Flux)
8. 动态范式 @Bean
这种类似于声明式的函数工具,Spring AI 通过 ToolCallbackResolver 接口(SpringBeanToolCallbackResolver具体实现),在运行时动态解析
可以将任意 Function、Supplier、Consumer 或 BiFunction 类型的 Bean 作为工具使用。
Bean名称将作为工具名称`Spring Framework的@Description注解提供工具描述
实测,没有成功,待后续确认这个逻辑是否和官网说的一致
三、小结
本篇文章主要介绍了SpringAI如何定义、使用工具调用,包括方法工具/函数工具两类,有基于@Tool注解的声明式,也有借助 MethodToolCallback 和 FunctionToolCallback 实现的编程式
在工具的定义上,我们需要额外关注工具的描述,传参和返回;其中传参是通过 Json Schema 的形式给到的大模型
默认行为时,Spring AI 会自动拦截模型的工具调用请求,执行工具并将结果返回模型。这些操作均由各 ChatModel 实现通过 ToolCallingManager 透明完成,如下图
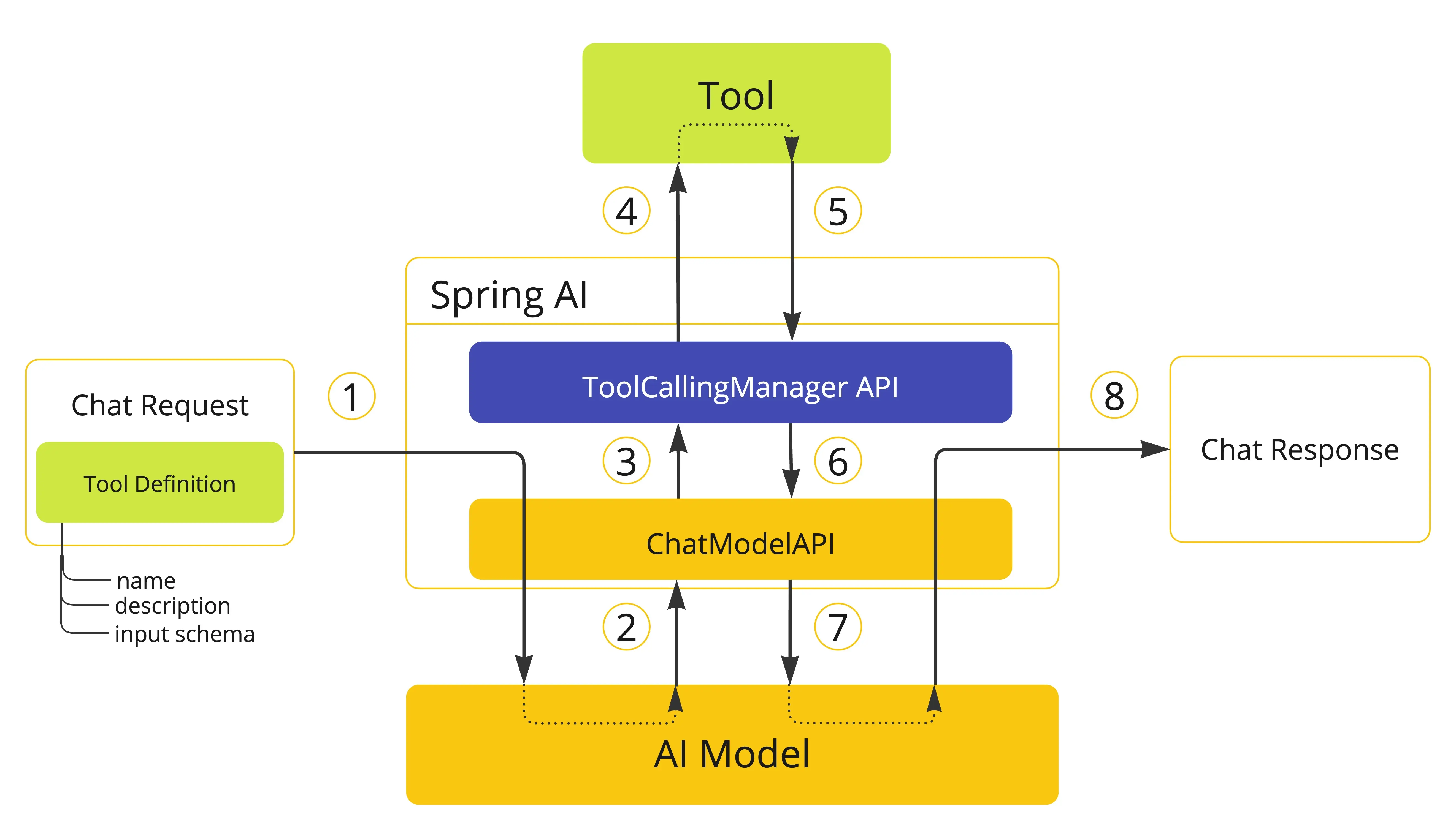
- 当需要向模型提供工具时,我们将其定义包含在聊天请求(Prompt)中,并调用 ChatModel API 将请求发送至 AI 模型。
- 当模型决定调用工具时,它会发送包含工具名称及符合定义模式的输入参数的响应(ChatResponse)。
- ChatModel 将工具调用请求发送至 ToolCallingManager API。
- ToolCallingManager 负责识别需调用的工具并使用提供的输入参数执行该工具。
- 工具调用结果返回至 ToolCallingManager。
- ToolCallingManager 将工具执行结果返回给 ChatModel。
- ChatModel 将工具执行结果返回AI模型(ToolResponseMessage)。
- AI 模型利用工具调用结果作为附加上下文生成最终响应,并通过 ChatClient 将其返回调用方(ChatResponse)。
目前与模型交互的工具执行,是由SpringAI托管的,内部的工具选择等逻辑对用户是不透明的,当然也可以通过将 ToolCallingChatOptions 的 internalToolExecutionEnabled 属性设为 false,来实现自行控制工具执行的生命周期;这块的内容,将在下一章节进行介绍
文中所有涉及到的代码,可以到项目中获取 https://github.com/liuyueyi/spring-ai-demo