4.自定义请求匹配条件RequestCondition
在spring mvc中,我们知道用户发起的请求可以通过url匹配到我们通过@RequestMapping定义的服务端点上;不知道有几个问题大家是否有过思考
一个项目中,能否存在完全相同的url?
有了解http协议的同学可能很快就能给出答案,当然可以,url相同,请求方法不同即可;那么能否出现url相同且请求方法l也相同的呢?
本文将介绍一下如何使用RequestCondition结合RequestMappingHandlerMapping,来实现url匹配规则的扩展,从而支持上面提出的case
I. 环境相关
本文介绍的内容和实际case将基于spring-boot-2.2.1.RELEASE版本,如果在测试时,发现某些地方没法兼容时,请确定一下版本
1. 项目搭建
首先我们需要搭建一个web工程,以方便后续的servelt注册的实例演示,可以通过spring boot官网创建工程,也可以建立一个maven工程,在pom.xml中如下配置
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/libs-snapshot-local</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/libs-milestone-local</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-releases</id>
<name>Spring Releases</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/libs-release-local</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
2. RequestCondition介绍
在spring mvc中,通过DispatchServlet接收客户端发起的一个请求之后,会通过HanderMapping来获取对应的请求处理器;而HanderMapping如何找到可以处理这个请求的处理器呢,这就需要RequestCondition来决定了
接口定义如下,主要有三个方法,
public interface RequestCondition<T> {
// 一个http接口上有多个条件规则时,用于合并
T combine(T other);
// 这个是重点,用于判断当前匹配条件和请求是否匹配;如果不匹配返回null
// 如果匹配,生成一个新的请求匹配条件,该新的请求匹配条件是当前请求匹配条件针对指定请求request的剪裁
// 举个例子来讲,如果当前请求匹配条件是一个路径匹配条件,包含多个路径匹配模板,
// 并且其中有些模板和指定请求request匹配,那么返回的新建的请求匹配条件将仅仅
// 包含和指定请求request匹配的那些路径模板。
@Nullable
T getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request);
// 针对指定的请求对象request发现有多个满足条件的,用来排序指定优先级,使用最优的进行响应
int compareTo(T other, HttpServletRequest request);
}
简单说下三个接口的作用
combine: 某个接口有多个规则时,进行合并- 比如类上指定了
@RequestMapping的url为root - 而方法上指定的
@RequestMapping的url为method - 那么在获取这个接口的url匹配规则时,类上扫描一次,方法上扫描一次,这个时候就需要把这两个合并成一个,表示这个接口匹配
root/method
- 比如类上指定了
getMatchingCondition:- 判断是否成功,失败返回null;否则,则返回匹配成功的条件
compareTo:- 多个都满足条件时,用来指定具体选择哪一个
在Spring MVC中,默认提供了下面几种
| 类 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| PatternsRequestCondition | 路径匹配,即url |
| RequestMethodsRequestCondition | 请求方法,注意是指http请求方法 |
| ParamsRequestCondition | 请求参数条件匹配 |
| HeadersRequestCondition | 请求头匹配 |
| ConsumesRequestCondition | 可消费MIME匹配条件 |
| ProducesRequestCondition | 可生成MIME匹配条件 |
II. 实例说明
单纯的看说明,可能不太好理解它的使用方式,接下来我们通过一个实际的case,来演示使用姿势
1. 场景说明
我们有个服务同时针对app/wap/pc三个平台,我们希望可以指定某些接口只为特定的平台提供服务
2. 实现
首先我们定义通过请求头中的x-platform来区分平台;即用户发起的请求中,需要携带这个请求头
定义平台枚举类
public enum PlatformEnum {
PC("pc", 1), APP("app", 1), WAP("wap", 1), ALL("all", 0);
@Getter
private String name;
@Getter
private int order;
PlatformEnum(String name, int order) {
this.name = name;
this.order = order;
}
public static PlatformEnum nameOf(String name) {
if (name == null) {
return ALL;
}
name = name.toLowerCase().trim();
for (PlatformEnum sub : values()) {
if (sub.name.equals(name)) {
return sub;
}
}
return ALL;
}
}
然后定义一个注解@Platform,如果某个接口需要指定平台,则加上这个注解即可
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface Platform {
PlatformEnum value() default PlatformEnum.ALL;
}
定义匹配规则PlatformRequestCondition继承自RequestCondition,实现三个接口,从请求头中获取平台,根据平台是否相同过来判定是否可以支持请求
public class PlatformRequestCondition implements RequestCondition<PlatformRequestCondition> {
@Getter
@Setter
private PlatformEnum platform;
public PlatformRequestCondition(PlatformEnum platform) {
this.platform = platform;
}
@Override
public PlatformRequestCondition combine(PlatformRequestCondition other) {
return new PlatformRequestCondition(other.platform);
}
@Override
public PlatformRequestCondition getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request) {
PlatformEnum platform = this.getPlatform(request);
if (this.platform.equals(platform)) {
return this;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 优先级
*
* @param other
* @param request
* @return
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(PlatformRequestCondition other, HttpServletRequest request) {
int thisOrder = this.platform.getOrder();
int otherOrder = other.platform.getOrder();
return otherOrder - thisOrder;
}
private PlatformEnum getPlatform(HttpServletRequest request) {
String platform = request.getHeader("x-platform");
return PlatformEnum.nameOf(platform);
}
}
匹配规则指定完毕之后,需要注册到HandlerMapping上才能生效,这里我们自定义一个PlatformHandlerMapping
public class PlatformHandlerMapping extends RequestMappingHandlerMapping {
@Override
protected RequestCondition<?> getCustomTypeCondition(Class<?> handlerType) {
return buildFrom(AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(handlerType, Platform.class));
}
@Override
protected RequestCondition<?> getCustomMethodCondition(Method method) {
return buildFrom(AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, Platform.class));
}
private PlatformRequestCondition buildFrom(Platform platform) {
return platform == null ? null : new PlatformRequestCondition(platform.value());
}
}
最后则是需要将我们的HandlerMapping注册到Spring MVC容器,在这里我们借助WebMvcConfigurationSupport来手动注册(注意一下,不同的版本,下面的方法可能会不太一样哦)
@Configuration
public class Config extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
@Override
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping(
@Qualifier("mvcContentNegotiationManager") ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager,
@Qualifier("mvcConversionService") FormattingConversionService conversionService,
@Qualifier("mvcResourceUrlProvider") ResourceUrlProvider resourceUrlProvider) {
PlatformHandlerMapping handlerMapping = new PlatformHandlerMapping();
handlerMapping.setOrder(0);
handlerMapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors(conversionService, resourceUrlProvider));
return handlerMapping;
}
}
3. 测试
接下来进入实测环节,定义几个接口,分别指定不同的平台
@RestController
@RequestMapping(path = "method")
public class DemoMethodRest {
@Platform
@GetMapping(path = "index")
public String allIndex() {
return "default index";
}
@Platform(PlatformEnum.PC)
@GetMapping(path = "index")
public String pcIndex() {
return "pc index";
}
@Platform(PlatformEnum.APP)
@GetMapping(path = "index")
public String appIndex() {
return "app index";
}
@Platform(PlatformEnum.WAP)
@GetMapping(path = "index")
public String wapIndex() {
return "wap index";
}
}
如果我们的规则可以正常生效,那么在请求头中设置不同的x-platform,返回的结果应该会不一样,实测结果如下
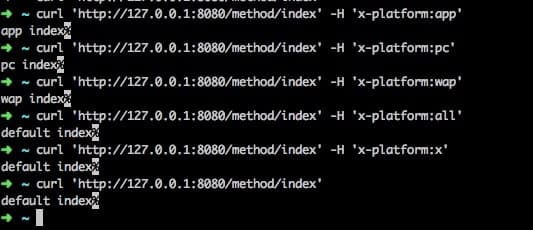
注意最后两个,一个是指定了一个不匹配我们的平台的请求头,一个是没有对应的请求头,都是走了默认的匹配规则;这是因为我们在PlatformRequestCondition中做了兼容,无法匹配平台时,分配到默认的Platform.ALL
然后还有一个小疑问,如果有一个服务不区分平台,那么不加上@Platform注解是否可以呢?
@GetMapping(path = "hello")
public String hello() {
return "hello";
}
当然是可以的实测结果如下:
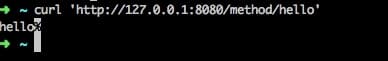
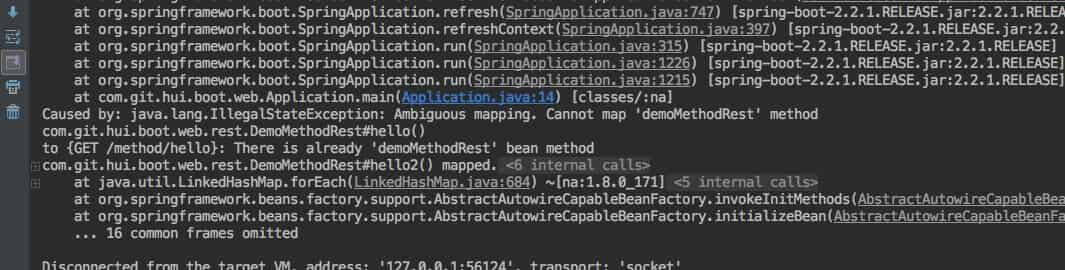
在不加上@Platform注解时,有一点需要注意,这个时候就不能出现多个url和请求方法相同的,在启动的时候会直接抛出异常哦
III. 其他
web系列博文
- 191206-SpringBoot系列教程web篇Listener四种注册姿势
- 191122-SpringBoot系列教程web篇Servlet 注册的四种姿势
- 191120-SpringBoot系列教程Web篇之开启GZIP数据压缩
- 191018-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之过滤器Filter使用指南扩展篇
- 191016-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之过滤器Filter使用指南
- 191012-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之自定义异常处理HandlerExceptionResolver
- 191010-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之全局异常处理
- 190930-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之404、500异常页面配置
- 190929-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之重定向
- 190913-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之返回文本、网页、图片的操作姿势
- 190905-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之中文乱码问题解决
- 190831-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之如何自定义参数解析器
- 190828-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之Post请求参数解析姿势汇总
- 190824-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之Get请求参数解析姿势汇总
- 190822-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之Beetl环境搭建
- 190820-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之Thymeleaf环境搭建
- 190816-SpringBoot系列教程web篇之Freemaker环境搭建
- 190421-SpringBoot高级篇WEB之websocket的使用说明
- 190327-Spring-RestTemplate之urlencode参数解析异常全程分析
- 190317-Spring MVC之基于java config无xml配置的web应用构建
- 190316-Spring MVC之基于xml配置的web应用构建
- 190213-SpringBoot文件上传异常之提示The temporary upload location xxx is not valid